How To Use Business Model Canvas
Updated by Xtensio
A well-developed business model canvas will help streamline planning, development, and execution across your business. It should align everyone’s objectives and eliminate inconsistencies between the various people who contribute to your business objectives. Use Xtensio’s free template to create your own without needing a professional designer! Explore this template.
Xtensio is your team space for beautiful living documents.
Create, manage and share business collateral, easily.
Table of Contents
Xtensio’s FREE Business Model Canvas Template and Editable Examples
Your starting point to create and share a successful brand positioning canvas, without any design experience.
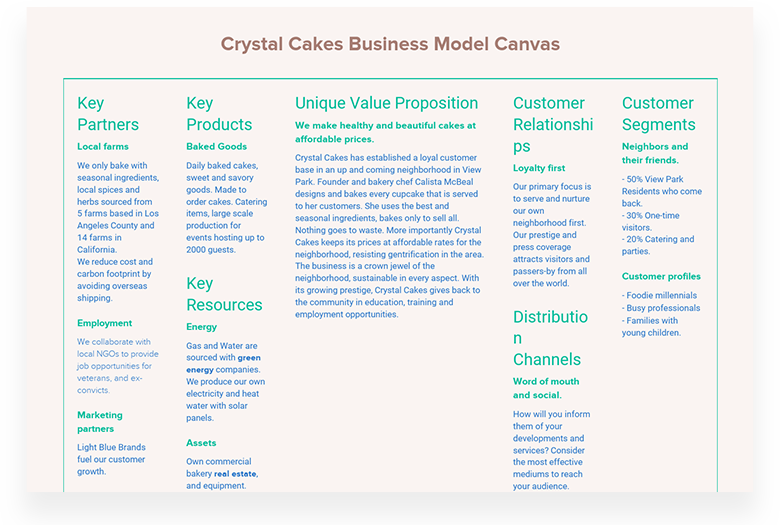
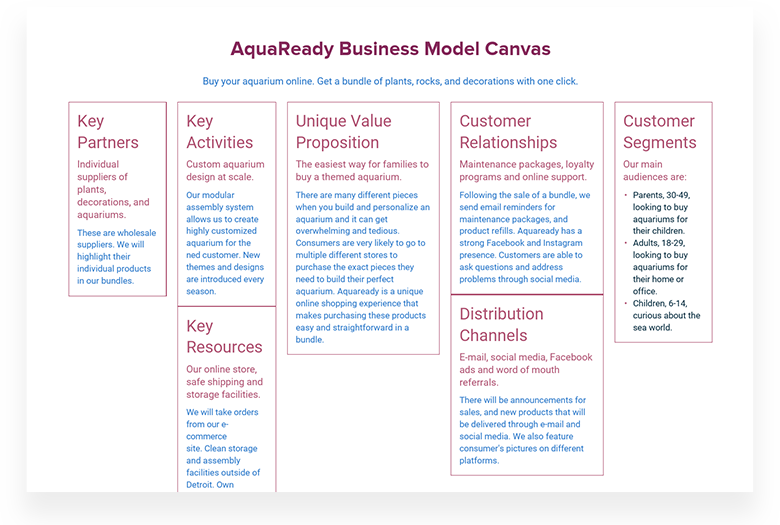
Key Partners
The first building block of your business model is to identify the key partners you need to conduct your business. Who would you like to have as your partners, suppliers, or collaborators on your business idea? It is helpful to target specific examples but it’s also helpful to have general lines of businesses you want to focus on.
Key Activities
What actions or activities do your value proposition require you to make? Identify the key steps you need to take in order for your business to deliver on its promises and make sure development rolls out smoothly. For a product-driven business, a key activity may be learning about users and how to build a better product. For an infrastructure business, it would be important to maintain that infrastructure and research ways to increase efficiency.
Key Resources
Consider what strategic assets you’ll need to begin and run your company. Use these tried-and-true frameworks to identify your key resources and find your differentiating factor among your competitors. For product-driven identify your core resources and discover what sets you apart from your competition. Specialized personnel in important areas of knowledge, such as experienced graphic designers and developers, as well as intellectual property, are critical resources for product-driven organizations. For scope-driven businesses or businesses that create synergy around a particular Customer Segment, it is important that key resources include knowledge about your target audience and a standard set of procedures for interaction and assistance with the group. For infrastructure-driven businesses, strategic assets could include the physical or virtual infrastructure involved with the business.
Fun Fact: A 2009 study conducted by IBM Institute for Business Value revealed that 7 out of 10 companies are engaging in “business-model innovation,” and an incredible 98% are modifying their business models to some extent. So even if you already have an existing business model, it’s beneficial to reevaluate it.

Unique Value Proposition
What is your business promising to its audience, and how does your product or service stand out? Carefully consider what is unique about your value proposition and why customers would prefer your product or service to alternative options. Then rank your propositions in relation to the needs of your customers. This will help you determine which value proposition is the highest priority and align your vision with your customers’ needs.
Your UVP statement should:
- Quickly and clearly convey the value of your service or product
- Explain how your product or service is better than the competition
- Talk about the benefits and features that define your product or service
- Avoid superlatives such as “the best” or “world-class”. Instead, include talking points that are carefully defined and factually correct
Go Deeper: Forbes suggests creating your UVP within the context of the 3Ds:
- Discontinuous innovations – offer transformative benefits over the status quo by looking at a problem differently
- Defensible technology – offer intellectual property that can be protected to create an unfair competitive advantage
- Disruptive business models – yield value and cost rewards that help catalyze the growth of your business
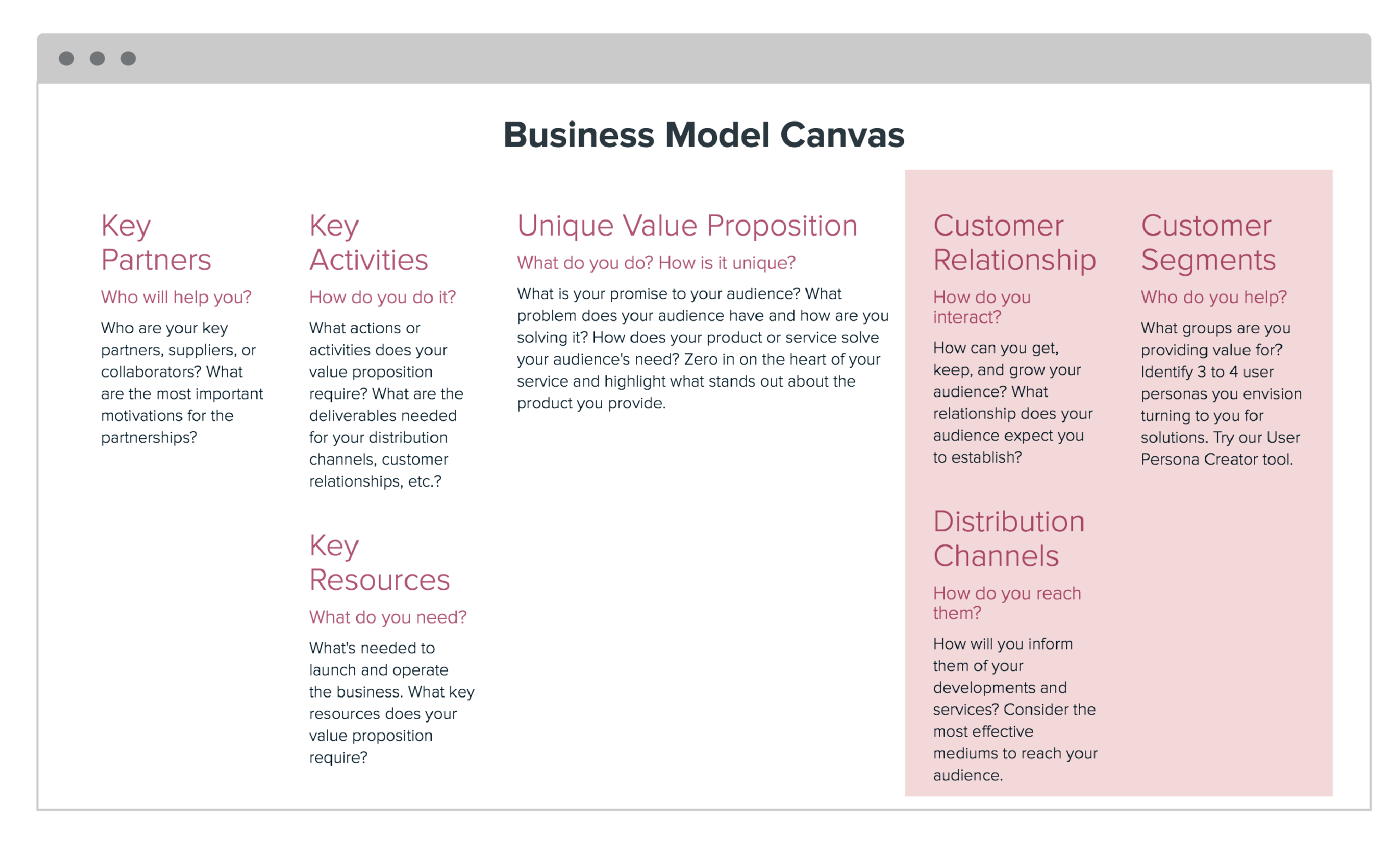
Customer Relationship
First, figure out how your customers will engage with your company. Do you deal with your consumers over the internet, do they have a personal relationship with a representative, or do you rely on customer service calls? It’s critical to lay down criteria for developing, maintaining, and growing your customer base after you’ve established the type of relationship.
Distribution Channels
What are the most effective mediums to reach your audience? What are the channels you use to communicate, sell, or provide service for customers? Make a list of the different channels that you plan on building a relationship with customers. Remember to think through the lens of the “customer journey.” The channels with which you grab a customer’s attention will be different from the way you onboard or support them.
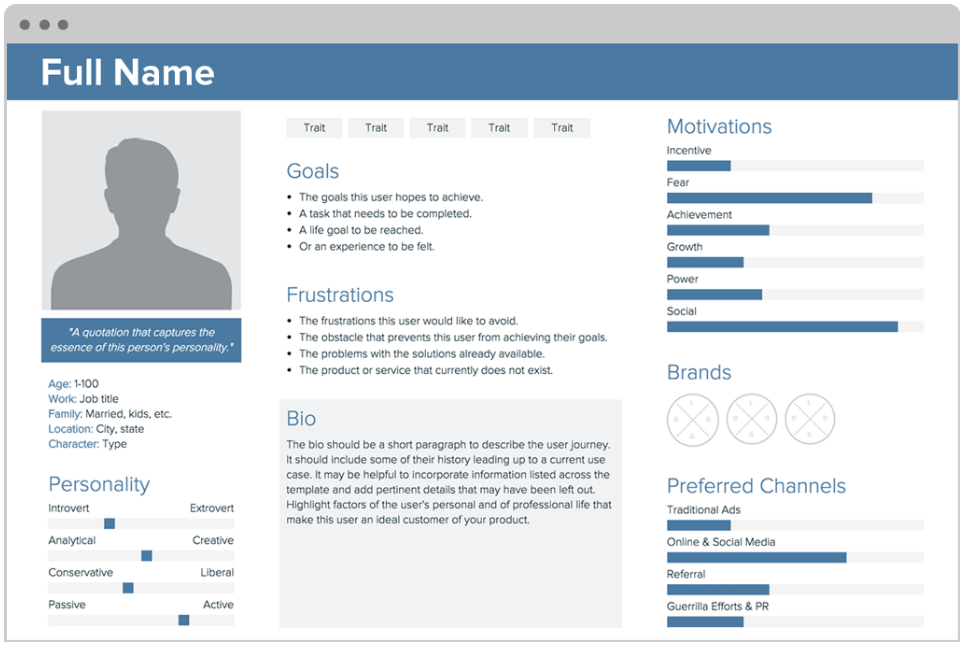
Customer Segments
In order to understand your customers, you need to understand several facets of your target segment. Is your customer segment a single or multi-sided market? Then you can move deeper to analyze who your individual customers are. Use our user persona template to create an in-depth analysis of your customer segments. With personas, you can investigate the problems and needs of your customers and use these insights to refine your business model.
Use personas to gain insight into your customer segments by
- Collecting and displaying information about your customers’ background, lifestyle, and behavioral practices
- Exploring the needs and desires of your customer and what they are using your product or service for
- Documenting the user journey
Bonus Tip: Use Google Analytics to quickly find consumer demographics. Collect data such as bounce rate, daily visits, visit duration, and any additional relevant information.
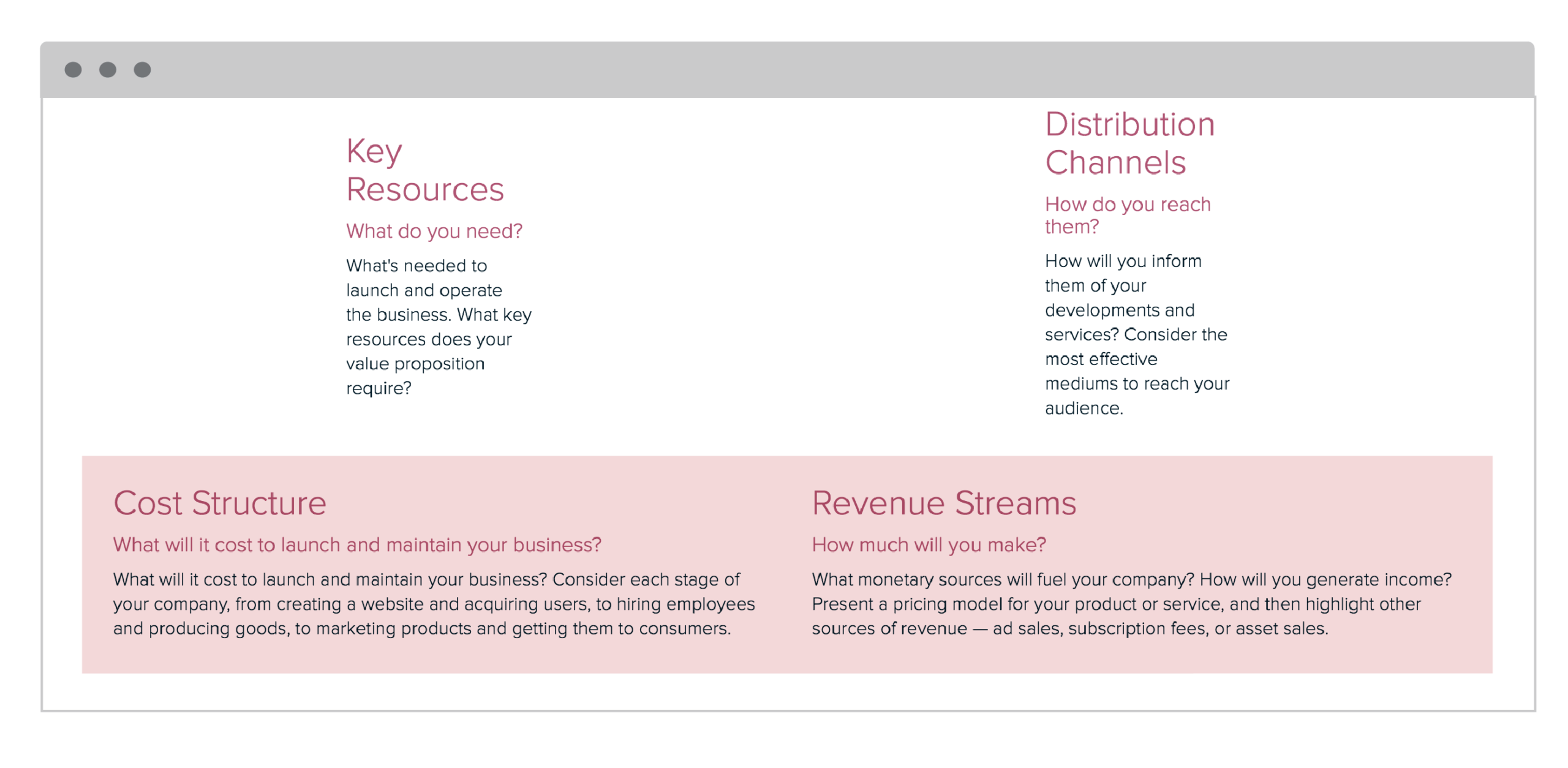
Cost Structure
Now that you’ve worked through the Key Activities, you have a better understanding of the actions your business needs to take. It’s time to think about how your Key Activities affect costs and whether they’re in line with your value propositions. It’s also crucial to think about the types of expenses your company may face. Are these costs set in stone or are they subject to change? Will your business’s costs be linear or fixed as it grows?
Revenue Streams
Take a careful look at your different customer segments and value propositions and mentally map out the patterns that may occur. For example, Persona 1 may engage with Value Proposition 1 and 2 or Persona 2 may engage with Value Proposition 2 and 3. Carefully look at where your business is driving revenue and whether it aligns with your value propositions.
Bonus Resource! George Washington University emphasizes the necessity of analyzing your answers to the business model before moving on to cost structure, pricing and quantity, and revenue models. They integrate a payment flow diagram and pricing strategy into their process in this slideshare.
Additional Resources
Remember, with Xtensio you can collaborate with anyone, anywhere in the world, and all of your folios are completely flexible — create it with the ease of a web builder, drag and drop building blocks. Share it like a web page, present it like a slideshow or download it as a PDF/PNG. Additionally, if you want to take a look at your business through a lean startup lens, you can use our lean canvas. And be sure to utilize our user personas to thoroughly investigate your customer segments.
List of free resources mentioned in this article

Design, manage and share beautiful living documents… easily, together. Explore Xtensio
- Click and edit anything… together.
- Customize to match your branding.
- Share with a link, present, embed or download.