What Is UX Design in 2024? A Comprehensive Guide to User Experience Design
Includes FREE Templates and Examples – 2024
Updated by Xtensio
Table of Contents
Welcome to the world of UX design in 2023! As technology continues to evolve, so does the importance of creating enjoyable, efficient, and relevant user experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of UX design, exploring its history, principles, differences from UI design, essential skills, tools, and techniques, and how you can build a successful career in this thriving field.
Short Summary
- UX Design is a user-centered process that involves incorporating usability, accessibility, and visual design principles.
- UX designers must possess technical skills such as wireframing, prototyping, and coding, as well as soft skills including empathy to create user-centered designs.
- Building a successful portfolio with diverse projects and detailed case studies showcasing the design process will help maximize success in the digital sector.
Understanding UX Design

UX design is the process of creating products that offer enjoyable, efficient, and relevant experiences for users, focusing on their needs, technical feasibility, and business viability. A user experience designer plays a crucial role in this discipline, which has grown significantly in importance as the digital landscape continues to expand and evolve. In fact, a well-crafted user experience can make all the difference in customer retention and satisfaction.
One of the key aspects of the UX design process is the constant feedback loop between designers and users. Through user testing and research, UX designers work diligently to understand how users interact with products and services, identifying pain points and areas for improvement. This iterative process is fueled by a deep understanding of human-system interaction, making UX design a critical component of any successful digital product or service.
The Evolution of UX Design
The field of UX design has its roots in human factors and ergonomics, with a focus on understanding user needs, goals, and mental models. Over time, UX design has evolved to encompass a wide range of disciplines, such as interaction design, information architecture, and user research. Today, UX designers must stay up-to-date on topics like human psychology, interaction design, and user research techniques to create seamless and enjoyable user experiences.
A crucial aspect of the UX design process is the Design Thinking Process, which involves four distinct stages.
- Inspiration
- Conceptualization
- Iteration
- Exposition
By following this process, UX designers can effectively identify user personas, gather valuable user feedback, and ultimately create user-centered designs that cater to the unique needs and preferences of their target audience.
Key Principles of UX Design
At the core of UX design are a set of key principles that guide the creation of user-centered products and services. Usability, accessibility, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design are all critical elements that contribute to the overall user experience. Usability, for instance, refers to the extent to which users can easily and effectively interact with a product or service, making it an essential aspect of human-system interaction.
Another vital principle in UX design is information architecture, which plays a crucial role in helping users achieve their goals and navigate through a product or service. By employing methods like card sorting, UX designers can map out user flows and create a user-centered design that caters to their needs and preferences.
Interaction designers, on the other hand, are responsible for understanding and defining how a product should respond, making them essential user interface designers in the UX design process.
UX vs UI Design: The Differences
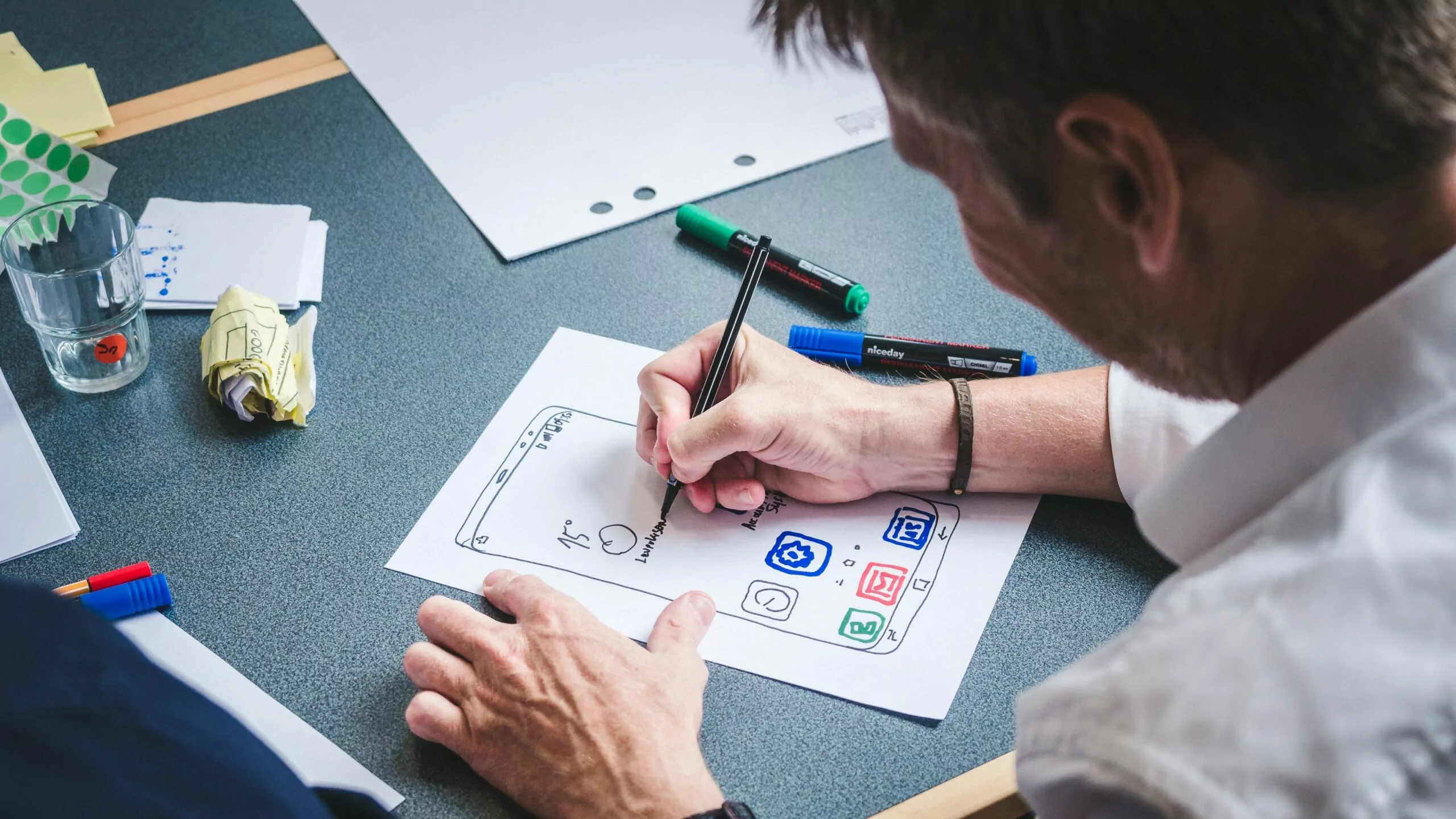

While both UX and UI design are critical components of creating seamless and enjoyable digital experiences, they each serve distinct roles in the design process. UX design focuses on the overall user experience and journey, ensuring that users can easily navigate and interact with a product or service. On the other hand, UI design is concerned with the visual and interactive elements of a product, such as colors, images, and symbols.
UX and UI designers often work closely together, collaborating to conduct user research, assess usability, and continually evaluate designs for potential successes or issues that need to be addressed. This collaboration requires a diverse set of skills, with UX designers focusing on aspects like user research, personas, and user flows, while UI designers concentrate on creating visually appealing and functional user interfaces.
UX Design Focus
The primary focus of UX design is understanding and catering to the needs and preferences of users. This involves:
- Conducting user research
- Developing personas
- Creating user flows to ensure a seamless and enjoyable user experience
- Gathering user feedback and understanding their goals, emotions, pain points, and behaviors
By following these steps, UX designers can create user-centered designs that truly resonate with their target audience.
In addition to understanding user needs, UX design also involves testing and iterating on designs to ensure they meet the desired objectives. Usability testing, focus groups, and other user research methods are employed to gather valuable insights and identify areas for improvement. Ultimately, the UX design process is centered around creating products and services that are enjoyable, efficient, and relevant to the end user.
UI Design Focus
UI design, on the other hand, is responsible for the aesthetics and functionality of the user interface. This includes the selection of colors, images, and symbols that make up the visual elements of a product or service. The primary goal of UI design is to create interfaces that users will find effortless to use and enjoyable to interact with.
In addition to the visual aspects of a product, UI design also involves creating interactive elements that allow users to engage with the product or service. This can include:
- Buttons
- Menus
- Sliders
- Other interface components
These elements facilitate user interaction and enable them to accomplish their desired tasks.
Overall, user interface design, also known as UI design, plays a crucial role in shaping the user’s experience with a product or service, ensuring that it is both visually appealing and functionally effective.
Essential Skills for UX Designers

To excel in the field of UX design, professionals must possess a unique blend of technical and soft skills. On the technical side, UX designers need to be proficient in ux design skills such as:
- Wireframing
- Prototyping
- Coding
- Familiar with various user research methods
These skills enable designers to effectively create and test designs, ensuring that they meet the needs and preferences of users.
Equally important are the soft skills that UX designers must possess. Some of these skills include:
- Empathy
- Organization
- Curiosity
- Effective communication
These skills are crucial for understanding user needs, collaborating with team members, and presenting ideas clearly and persuasively.
By cultivating both technical and soft skills, UX designers can create user-centered designs that truly resonate with their target audience.
Technical Skills
Technical skills are a cornerstone of UX design, enabling designers to effectively create, test, and refine their designs. Among these skills are wireframing and prototyping, which allow designers to visualize and iterate on their ideas before investing time and resources in development. By creating wireframes and prototypes, UX designers can quickly test the structure and functionality of their designs, ensuring that they meet user needs and expectations.
Another essential technical skill for UX designers is coding. While not all designers are required to be proficient in coding languages, having a basic understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can be invaluable. This knowledge enables designers to effectively communicate with developers and assess the feasibility of their design ideas, ensuring that the end product is both functional and visually appealing.
Soft Skills
In addition to technical expertise, UX designers must also possess a range of soft skills that enable them to effectively communicate, collaborate, and empathize with users. Among these skills are empathy, which allows designers to truly understand the needs, preferences, and pain points of their users, and organization, which helps designers manage their work and effectively collaborate with team members.
Curiosity and effective communication are also key soft skills for UX designers. A curious mindset encourages designers to constantly seek new insights and explore innovative solutions, while strong communication skills enable them to present their ideas clearly and persuasively. By cultivating these soft skills, UX designers can better understand user needs and create designs that truly resonate with their audience.
Tools and Techniques in UX Design

To bring their designs to life, UX designers utilize a variety of tools and techniques throughout the design process. Some of these tools and techniques include:
- Wireframing and prototyping tools that help visualize and test ideas
- User research methods that provide valuable insights into user needs and preferences
- Usability testing to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of a design
- Information architecture tools to organize and structure content
- Interaction design tools to create interactive and engaging user experiences
- Visual design tools to create visually appealing interfaces
- Collaboration tools to facilitate communication and collaboration among team members
These tools and techniques play a crucial role in the creation of user-centered designs.
Usability testing programs are another valuable resource for UX designers, allowing them to assess the usability of their designs and pinpoint areas for improvement. By employing a range of tools and techniques, UX designers can create products and services that are not only visually appealing but also functionally effective and enjoyable for users to interact with.
Wireframing and Prototyping Tools
Wireframing and prototyping tools are essential for UX designers, as they enable them to quickly visualize and iterate on their ideas, testing structure, and functionality before moving into production. These tools can range from low-fidelity options, which are used to create basic wireframes and prototypes, to high-fidelity tools that allow for more detailed and interactive prototypes.
Some widely used wireframing and prototyping tools include:
- Adobe XD
- Figma
- InVision
- Balsamiq
By utilizing these tools, UX designers can effectively test their designs, identify potential issues, and refine their ideas, ultimately creating user-centered products and services that meet the needs and preferences of their target audience.
User Research Methods
User research is a vital component of UX design, as it provides insights into user needs, preferences, and behaviors. UX designers employ various user research methods, such as:
- interviews
- surveys
- questionnaires
- focus groups
These methods help designers gain a deeper understanding of their users and create designs that truly resonate with them.
In addition to these traditional research methods, UX designers also utilize more advanced techniques, such as card sorting, heat maps, and user behavior analytics (UBA), to gather valuable data and inform their design decisions. By employing a diverse array of user research methods, UX designers can create user-centered designs that cater to the unique needs and preferences of their target audience.
How to Become a UX Designer

For those looking to enter the exciting world of UX design, there are several paths to consider. Some options include:
- Intensive UX design bootcamps that offer hands-on training and portfolio building
- Traditional degree programs that provide in-depth study of UX design theory
- Self-guided learning resources that allow individuals to learn at their own pace
There is an option to suit every aspiring UX designer’s needs and preferences.
Regardless of the path chosen, it’s important for aspiring UX designers to cultivate a strong foundation in both technical and soft skills, such as:
- Design thinking
- User research
- Prototyping
- Coding
- Communication
- Empathy
- Curiosity
By developing these skills and gaining practical experience, individuals can build successful careers in the thriving field of UX design.
UX Design Bootcamps
UX design bootcamps offer a fast-paced, hands-on approach to learning the skills necessary to succeed in the field. These comprehensive programs typically provide practical instruction, portfolio development, and professional career guidance for those seeking to transition into UX design. With a focus on real-world projects and collaboration, bootcamps equip participants with the skills and experience needed to hit the ground running in their new careers.
The demand for bootcamp graduates is on the rise, with one in three hiring managers having hired a bootcamp participant, and 72% of them feeling that bootcamp graduates were adequately or better prepared for their roles. As a result, UX design bootcamps are becoming an increasingly popular option for aspiring UX designers looking to break into the field.
Traditional Degree Programs
In addition to bootcamps, traditional degree programs offer another pathway for those looking to become UX designers. These programs provide a more in-depth exploration of UX design theory and related topics, such as human-system interaction, information architecture, and interaction design. Degree programs in UX design include Bachelor of Science in Information with a UX Design path, Bachelor of UX Design, and online BA in Graphic Design and Media Arts with a concentration in UX Design.
While these programs may take longer to complete compared to bootcamps, they offer a well-rounded education and a deeper understanding of the theoretical underpinnings of UX design. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals looking to pursue advanced roles in the field or those seeking a more traditional educational experience.
Self-Guided Learning Resources

For those looking to learn UX design at their own pace, self-guided learning resources offer a flexible and accessible option. These resources, which include online courses, educational apps, and videos, allow individuals to gain knowledge of UX design basics and develop their skills over time. Some popular self-guided learning resources for UX design include thefutur.com’s free resources, CareerFoundry’s UX Design Short Course, The Gymnasium’s UX Fundamentals, Accenture’s Digital Skills: User Experience on Future Learn, and ADPList’s self-guided class ‘The Guide to Design’.
By taking advantage of these self-guided learning resources, aspiring UX designers can build a strong foundation in UX design principles and techniques, ultimately preparing themselves for a successful career in the field.
Building a Successful UX Design Portfolio
A successful UX design portfolio is a critical component of any UX designer’s professional toolkit. Showcasing a designer’s skills, experience, and unique approach to problem-solving, a well-crafted portfolio can make all the difference when it comes to landing job opportunities and attracting clients. As the digital design sector is predicted to experience a growth rate of 11% by 2029, and the median remuneration for a digital designer in 2020 was $77,200, having a standout portfolio is essential for success in this thriving field.
To create a successful UX design portfolio, it’s important to include:
- A diverse range of projects that demonstrate your capabilities
- Detailed case studies that showcase your design process from research to final product
- Visually appealing and organized presentation of your work
- Highlighting your design thinking, problem-solving abilities, and unique approach to UX design
What to Include
When building a UX design portfolio, it’s important to include a variety of projects, case studies, and examples of your design process. This can range from wireframes and prototypes to user research results and final products. By showcasing a diverse range of work, you can demonstrate your versatility and expertise in various aspects of UX design.
In addition to showcasing your projects, it’s also important to provide context and explain the rationale behind your design decisions. This can include details about the user research conducted, the challenges faced, and the solutions proposed. By providing this information, you can give potential employers and clients a deeper understanding of your design process and problem-solving abilities.
Presenting Your Work
Presenting your work in a visually appealing and organized manner is crucial for making a strong impression with your UX design portfolio. A clear structure, such as a grid or hierarchy, can help guide the viewer’s eye and make it easy for them to navigate your portfolio. Consistent design elements, such as typography, colors, and imagery, can also help create a cohesive and professional look.
Additionally, it’s important to highlight the impact of your work, including any quantifiable outcomes, such as increased user engagement or improved user satisfaction, as well as any qualitative feedback you’ve received. By showcasing the value of your work and presenting it in an organized and visually appealing manner, you can effectively demonstrate your skills and expertise as a UX designer.
Summary
As technology continues to evolve, the importance of UX design in creating enjoyable, efficient, and relevant user experiences cannot be overstated. With a strong foundation in both technical and soft skills, as well as a diverse range of tools and techniques at their disposal, UX designers play a crucial role in shaping the digital landscape. Whether you’re just starting your journey into UX design or looking to take your skills to the next level, this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights and resources to help you navigate the exciting world of UX design in 2023.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is UX design like coding?
No, UX design does not require coding knowledge or expertise. However, having a basic understanding of coding and software development can help inform more efficient work and better designs.
Is UX design a hard career?
Becoming a UX designer may require some advanced skills and a certain amount of effort, but it is achievable. With the right training and portfolio, you can acquire the necessary design and research abilities to become successful.
By taking courses in user experience design, you can learn the fundamentals of UX design and how to apply them to real-world projects. You can also gain experience by working on personal projects and building relationships.
Do UX designers make money?
Yes, UX designers make good money. Glassdoor reports that UX designers in the UK earn an average of £32,957, while those in the US have an average salary of $94,560.
This shows that UX design is a lucrative career path for those who are interested in the field. With the right skills and experience.
Is UX design a stressful job?
Overall, UX design is a rewarding and enjoyable career choice for many professionals. However, it can also come with stressors that need to be managed in order to avoid potential burnout.
What exactly does a UX designer do?
A UX designer’s priority is to ensure user satisfaction by continuously improving the product, such as making it faster, easier to use, or more enjoyable.
These improvements can range from small tweaks to major overhauls, depending on the product and the user’s needs. The designer must also be aware of the latest trends and technologies in order to stay ahead of the competition.